SLA Setup in R12 with a simple example for Payables
Subledger Accounting:
SLA is a new concept in R12, where all the accounting information and
rules are defined. Accounting entries generated in Subledgers are first
transferred to SLA and then interfaced to GL. Hence reconciliation is
already done in SLA before transferring to GL.
One big advantage in SLA is to configure rules to derive different
accounting entries. Each and every segment for different accounting
events could be configured to suit different business requirements which
was not possible in 11i.
Liability account in payables would be defaulted from supplier site on
to the invoices in 11i. If individual segments need to be different for
different business, then custom programs were required. In SLA, we can
set different rules to derive different segments for the liability
account.
We shall see how we can derive the liability account based on one
business requirement(to derive cost center based on invoice currency).
We will be using the below functionalities to achieve the purpose.
Journal Line Type
Mapping Sets
Account Derivation Rules
Journal Lines Definition
Application Accounting Definition
Subledger Accounting Method
Then assigning the Subledger Accounting Method to the Ledger.
In our example we shall make use of the copy functionality provided by
Oracle where ever available to derive our own custom types.
For complete definition of SLA and its components please refer to Oracle SLA Implementation guide.
The chart of accounts considered in the below example has 5 segments.
Company, Cost Center, Account, Analysis, Others. Also automatic offset
is enabled and set as 'Balancing' for the Operating Unit considered
Journal Line Type:
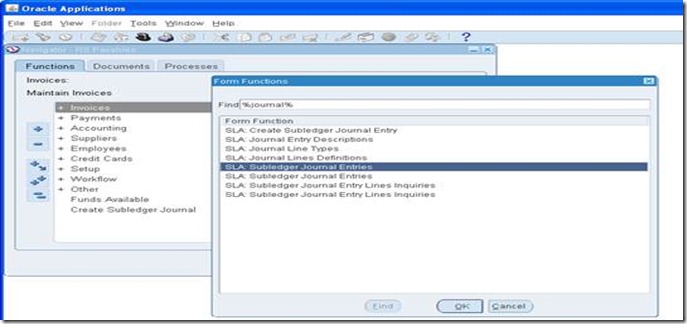
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Journal Entry Setup --> Journal Line Types
Journal types are defined for a particular event class(like invoices,
credit memos..) and assigned to journal line definition along with
mapping sets, account derivation rules.
We shall use the Oracle seeded Journal Line Type ‘Liability with
Automatic Offsets Balancing Segment’ to make our custom line type.
Open the Journal Line Types window and query for ‘Liability with Automatic Offsets Balancing Segment’.
Click on copy, give our custom name.
‘XX Liab with Automatic Offsets Balancing Segment’
Click on Conditions, it would be same as the seeded Oracle Journal Line Type
The conditions are specified to create a Journal Entry based on this Journal Line Type when certain conditions are met.
The conditions in the above screenshot mentions the Journal Line Type to
be created when Automatic Offset is set to ‘Balancing’ and for
different invoice types.
Our requirement is to derive the cost center based on the invoice
currency code. We shall see how we can achieve this using Mapping Sets
and Account Derivation Rules.
Mapping Sets:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Journal Entry Setup --> Mapping Sets
Mapping sets are used to get an output value for a particular segment or entire accounting flexfield based on input value.
Open mapping sets, click on New. Create new mapping set ‘XX Liability CC Map’.
In the input region, we have specified AP_SRS_CURRENCY valueset which
will restrict the input value to valid currencies. In the output section
we have selected the Chart of accounts and selected the segment as
‘Cost Center’.
In the mapping set values we have selected input value as ‘EUR’ and the output cost center.
Account Derivation Rules:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Journal Entry Setup --> Account Derivation Rules
Account derivation rules are used along with Mapping sets to derive the accounting flexfield or individual segments.
Open ‘Account Derivation Rules’, click on ‘New’. Create Account derivation rule ‘XX LIABILITY CC ADR’
Select the Output Type as Segment and select ‘Cost Center’ segment. In
priorities region, give the value type as ‘Mapping Set’ and value as ‘XX
Liability CC Map’ which was created earlier. Select the input source as
‘Invoice Currency Code’
Journal Line Definition:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Methods and Definition --> Journal Lines Definition
Journal line definition is used to assign journal line types for an
event class or event type. This is where the Account Derivation rule is
assigned to a journal line type.
Instead of creating an entirely new Journal Line Definitions, we shall
make use of the copy definition functionality provided by Oracle.
Open the ‘Journal Lines Definition’. Query for event class ‘Invoices’,
event type ‘All’ and definition code ‘ACCRUAL_INVOICES_ALL’.
Click on ‘Copy Definition’, give the definition code as
‘XX_ACCRUAL_INVOICES_ALL’, name as ‘XX Accrual Invoices All’. Select
transaction and accounting chart of accounts as ‘Accounting Flexfield‘.
Click on Done
In the ‘Line Assignments’ region disable ‘Liability with Automatic
Offsets Balancing Segment‘ line type. Add the Journal Line Type Created –
‘XX Liab with Automatic Offsets Balancing Segment’.
In the Account Derivation Rules tab, select ‘All Segments’ and assign
the standard Account Derivation Rule ‘Liability’. Select ‘Company’
segment and choose ‘Inherit’. Assign the Account Derivation rule created
‘XX Liability CC ADR’ to the segment ‘Cost Center’.
Application Accounting Definitions:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder -->
Methods and Definition --> Application Accounting Definitions
Application accounting definition is used for assigning Journal Line Definitions to event classes and types.
We shall use copy functionality provided by Oracle to copy the Application Accounting Definition and make modifications.
Open ‘Application Accounting Definition’ and query for definition code ‘ACCRUAL’.
Click on Copy. Give the definition code ‘XX ACCRUAL’ and definition name
as ‘XX Accrual Basis’. Select the transaction and accounting chart of
accounts as ‘Accounting Flexfield’. Click on done. For the event class
‘Invoices’, delete the default journal line definition assigned and
assign the Line Definition created earlier ‘XX Accrual Invoices All’.
Click on validate and make sure it is validated.
Subledger Accounting Method:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Methods and Definition --> Subledger Accounting Methods
Application Accounting Definitions defined are assigned to different
applications in Subledger Accounting Method. Subledger Accounting Method
is then assigned to the ledger.
Open the Subledger Accounting Method. Click on New. Give the method code
as ‘XX_STANDARD_ACCRUAL’ and method name as XX Standard Accrual. Select
the transaction and accounting chart of accounts as ‘Accounting
Flexfield’. In the Application Accounting Definition Assignment region
assign ‘XX Accrual Basis’ for Payables.
The Subledger accounting method is attached to the ledger.
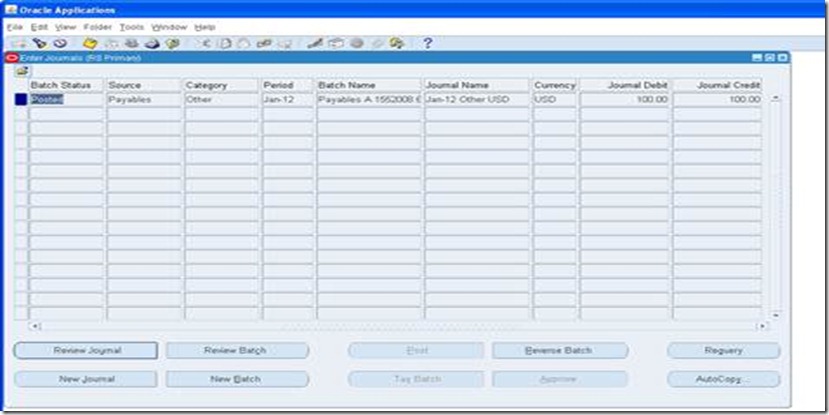
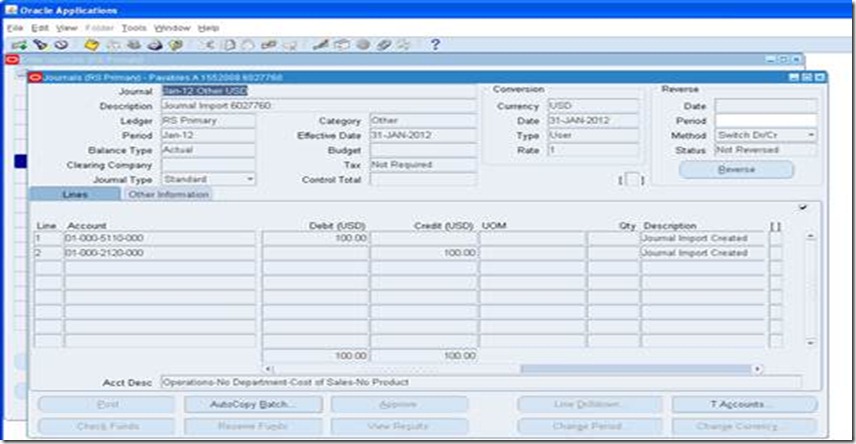
Create an invoice with currency code as ‘EUR’, validate and account the
invoice. Check for the accounting entries created. The liability account
would be having the cost center segment as ‘000000000EUR’.
Supporting
references can be defined to store additional information on the
subledger journal header or line level. The additional information could
be transaction information like invoice type or line type, or
accounting information or any supplier information etc. Supporting
references can then be used for finding the subledger balance for the
defined reference for a given period.
We
shall see the process of creating a supporting reference and assigning
it to journal line definition, creating an invoice and checking the
supporting reference in the subledger journal entries after accounting.
The below mentioned supporting reference is for AP Invoice Distribution
Type.
Define Supporting Reference:
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Journal Entry Setup --> Supporting References
Click on Create.
Give
the code as XX_DISTTYPE_SR, name as XX Dist Type SR, description as
‘Supp Ref for distribution line type’. Select ‘Enabled’ flag and
‘Maintain Balances’ which will enable us to check the subledger balance
for the Supporting reference. Select year end carry forward as ‘Never’.
Click on ‘Add Detail’ in the ‘Supporting Reference Detail’ section.
Upto five details can be added to a supporting reference. Give the Code as ‘DISTTYPE’, name as ‘Distribution Type’.
Click
on ‘Assign Sources’. In the search section, select application name as
‘Payables’ and source name as ‘Invoice Distribution Type’. Click on Go,
in the search results select ‘Invoices’ in the Event Class Name. Click
on ‘Apply’.
Assign Supporting Reference to the Journal Line Definition.
Subledger Accounting Setup --> Accounting Methods Builder --> Methods and Definition --> Journal Lines Definition
Query
for the Journal Line Definition for the event class ‘Invoices’, in the
journal line type select the ‘Liability’ . Go to the supporting
references tab and assign the supporting reference ‘XX Dist Type SR’.
Validate the Application Accounting Definition.
Create an invoice, validate and do accounting.
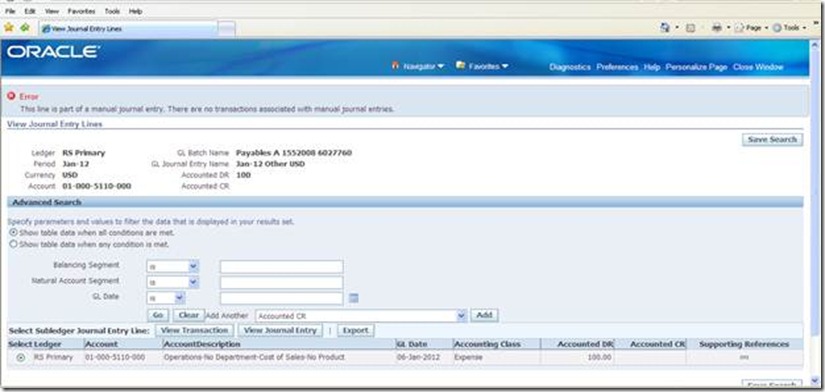
Check the journal lines created.
Click on the supporting references for the Liability
Check
the supporting reference details. Supporting reference has been created
with Detail Name as 'Distribution Type' and value as 'Item', which is
the invoice distribution line type.
Supporting Reference Balances
We can check the balances for the supporting reference in the Supporting Reference Balances. Run the ‘Subledger Accounting Balances Update’ program.
Subledger Accounting -> Supporting Reference Balances
Query for the supporting reference